If you are interested in breast surgery with implants, it is important to know the different positions where breast implants can be placed. By learning about the different implant placements available, you will be able to better understand your surgeon during consultation and make an informed decision about your breast surgery.
In this blogpost, we will explain the three main breast implant placements as well as their main benefits and disadvantages.
An intro guide to the breast
To better understand the different ways breast implants can be placed inside the breast, we first need to learn some anatomy basics.
The breast is comprised of three types of tissue: fibrous, glandular, and fatty: (1, 2)
- Glandular tissue is the tissue responsible for producing milk, usually shaped in lobes. Milk leaves through tubes called ducts, which end at the nipple.
- Fibrous tissue holds glandular and fatty tissues in place. Together, fibrous and glandular tissue are called fibro-glandular tissue.
- Fatty tissue fills the space between fibrous and glandular tissues and gives the breasts their size and shape.
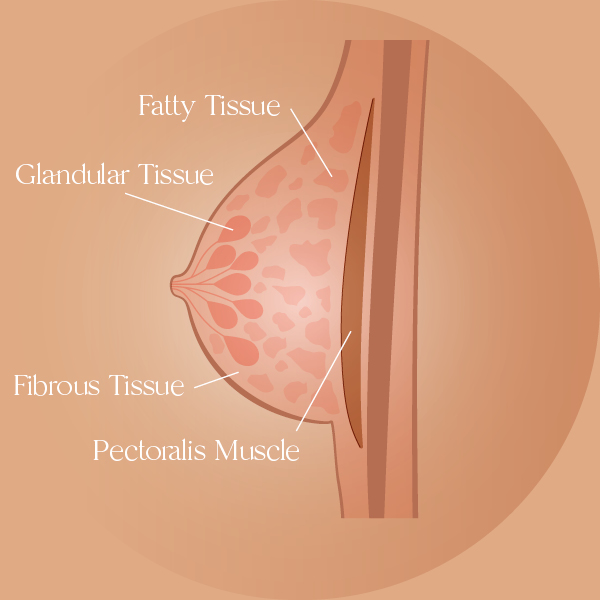
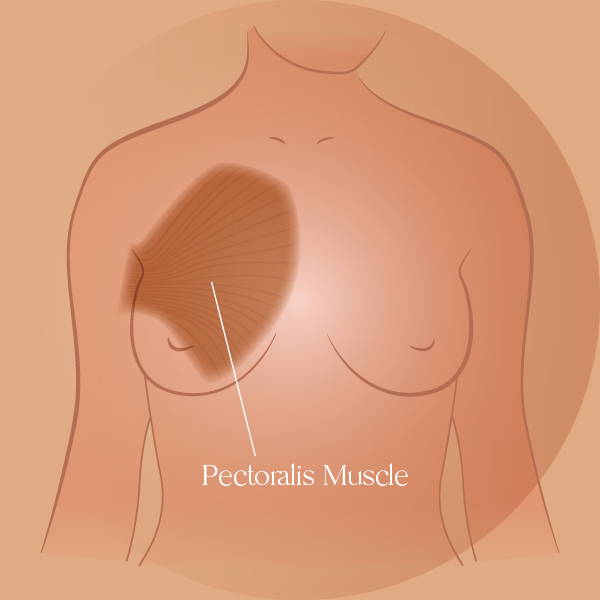
Under the tissues described above, the chest also includes muscles, such as the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor. In this article, we will focus on the pectoralis major, which is the largest muscle in the chest. (3)
The pectoralis major is a large fan-shaped muscle (as seen in the image below). It stretches from the armpit up to the collarbone and down across the lower chest region on both sides of the chest. (3)
The pectoralis major is enclosed by the fascia, a sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, that encloses, and separates muscles.(4)
Understanding How Breast Implants Are Placed
During breast augmentation surgery, a breast implant can be positioned either directly behind the breast tissue (sub-glandularly), under the fascia of the muscle (sub-fascially) or below the pectoral muscle (sub-pectoral or sub-muscular). Your surgeon will advise you on which placement is best suitable for you. POLYTECH silicone implants are soft and adapt to their placement, whether positioned sub-glandularly, sub-fascially or sub-muscularly.
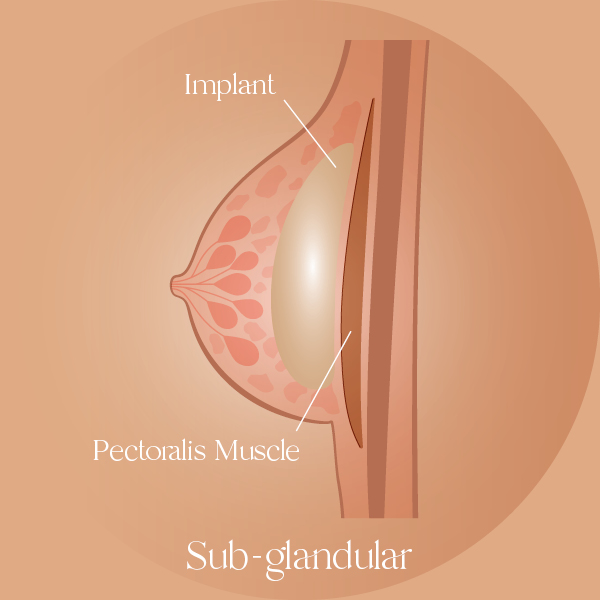
Sub-glandular position
In the sub-glandular placement, the implant is positioned above the pectoral muscle, but under the breast tissues (as seen in the image below).
This placement has a main benefit: it requires less dissection, so it is the easiest placement to perform, and normally recovery is more comfortable and quicker. (5)
The sub-glandular position also has some disadvantages that need to be considered: in women who do not have sufficient natural breast tissues to offer coverage, the implants may be more visible or palpable.(5) With this placement, performing mammograms can be more more challenging. (5)
Surgeons may choose this placement for women who have a larger amount of natural breast tissues that provide good coverage of the implant. (5)
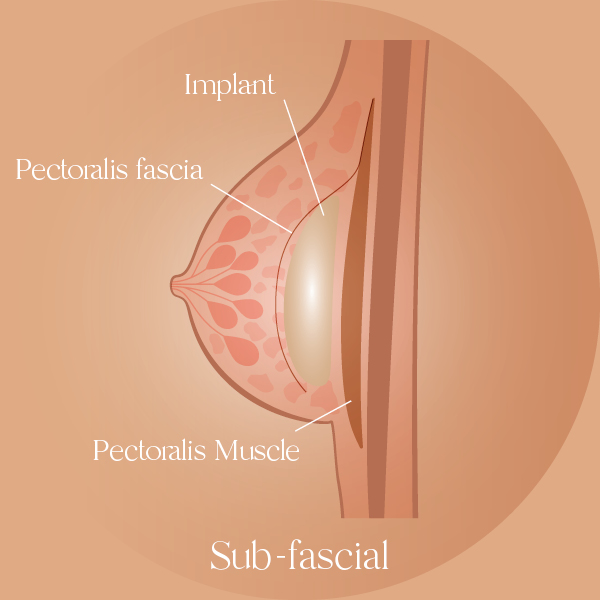
Sub-fascial
In the sub-fascial placement, places the implant above the pectoralis muscle but below the pectoralis fascia (as seen in the image below).
According to a study performed in 2020 (6), this position may provide the benefits of low rates of capsular contracture while avoiding the discomfort and possible future deformity of a sub-muscular placement. (6)
With this placement, there is also less implant edge visibility and palpability, seen most with the sub-glandular placement. (7, 8) Reports also show lower rates of capsular contracture. (7, 8, 9)
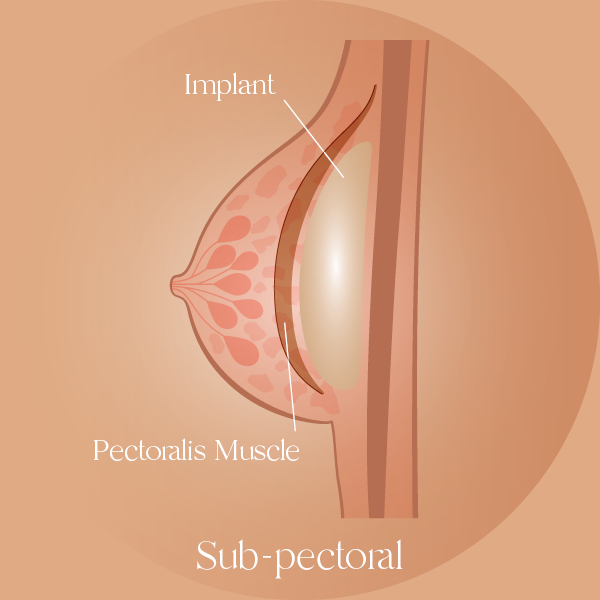
Sub-pectoral or sub-muscular placement
In the sub-pectoral or sub-muscular placement, the implant is placed directly behind the pectoralis major muscle and underneath the supporting tissues (as seen in the image below).
This method allows for more natural results in the upper pole since there is more tissue coverage. (5)
This placement is also associated with a slightly decreased risk of capsular contracture.(5)
While mammograms are safe to perform with all types of placements, the sub-muscular placement is considered beneficial for mammograms, as the implant rests behind the tissues, which facilitates mammogram views of such tissues. (5)
There are some drawbacks to this placement that need to be considered: recovery may be less comfortable and swelling may take longer to subside due to the incision made in the muscle. This means that results from the procedure may also take slightly longer to settle. (5)
Which placement is for me?
The decision of which placement is best for you will be taken by your surgeon. Some factors that may help him or her determine the right placement for you, include (4):
- Your body type and existing breast tissue
- The size and shape of the implants chosen
- Your goals and preferences for your breast results
We hope this guide serves as a basic starting point to understand your options and the terminology used by your surgeon. Don’t hesitate to raise your questions if you have any doubts about the placement suggested by your medical team. It is important that you feel safe and content about all aspects of your breast surgery.
SOURCES
(1) https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/basic_info/dense-breasts.htm
(2) https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/types/breast/anatomy-breast
(3) https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/female-chest-muscles#1
(4) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fascia
(5) Hidalgo DA, Spector JA. Breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014 Apr;133(4):567e-583e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000033. PMID: 24675209.
(6) Daniel J Gould, MD, PhD, Orr Shauly, BS, Levonti Ohanissian, BS, W Grant Stevens, MD, Subfascial Breast Augmentation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Capsular Contracture, Aesthetic Surgery Journal Open Forum, Volume 2, Issue 1, January 2020, ojaa006, https://doi.org/10.1093/asjof/ojaa006https://academic.oup.com/asjopenforum/article/2/1/ojaa006/5724437
(7) Graf RM, Bernardes A, Rippel R, Araujo LR, Damasio RC, Auersvald A. Subfascial breast implant: a new procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003 Feb;111(2):904-8. doi: 10.1097/01.PRS.0000041601.59651.15. PMID: 12560720. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12560720/
(8) Sabadin Heboni et al. “Augmentation Mammoplasty by Subfascial Technique.” Revista Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica (RBCP) – Brazilian Journal of Plastic Sugery 36.3 (2021): 244–248. https://www.scielo.br/j/rbcp/a/rvdxJFcSTX33LBscZGxNfXk/?lang=en
(9) Elizondo, V., & Elizondo, R. A. (2012). Capsular contracture in subfascial breast augmentation: recommendations and treatment. European Journal of Plastic Surgery, 35(7), 527–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00238-011-0682-Y
